Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses need to stay ahead of the curve to effectively reach and engage with their target audience. SMS short codes have emerged as a game-changer in modern communication, offering a powerful tool for businesses to connect with customers, drive conversions, and boost brand loyalty. With their convenience, speed, and reach, sms short codes have become an essential component of successful marketing strategies.
However, navigating the complex world of short codes requires expertise and knowledge of best practices to avoid common mistakes and ensure compliance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of sms short codes, exploring their benefits, types, and use cases, as well as providing expert insights and actionable tips to help you harness the full potential of short codes and take your communication strategy to the next level.
What are SMS Short Codes?
SMS short codes are special phone numbers used for sending and receiving SMS messages. They are typically 5-6 digits long and are used for various purposes, such as marketing campaigns, customer support, and alerts. Short codes are also known as short numbers or short codes.
Brief History and Evolution of Short Codes
Short codes have been in use since the early 2000s, when mobile marketing first started gaining popularity. Initially, short codes were used primarily for simple SMS campaigns, but as mobile technology evolved, so did the use cases for short codes electronic SMS communication. Today, short codes are used for a wide range of applications, from customer engagement to transactional messaging.
Importance of SMS Short Codes
SMS short codes play a crucial role in modern communication, offering several benefits for businesses and individuals:
- Convenience: Short codes are easy to remember and use, making them ideal for marketing campaigns and customer support.
- Speed: Short codes enable fast and efficient communication, allowing businesses to quickly reach their target audience.
- Reach: Short codes can be used to reach a large audience, making them ideal for mass marketing campaigns.
How SMS Short Codes Work
SMS short codes work by using a combination of technology and carrier partnerships to enable the sending and receiving of SMS software. Here’s a simplified overview of the process:
- Message Submission: A business or individual submits an SMS message to a short code.
- Message Routing: The message is routed through a Short Message Service Center (SMSC) to the relevant carrier.
- Carrier Delivery: The carrier delivers the message to the recipient’s mobile device.
- Response Handling: If the recipient responds to the message, the response is routed back through the SMSC to the original sender.
Short Code Types
There are three main types of short codes:
- Dedicated Short Codes: Exclusive to a single business or organization, offering full control and customization.
- Shared Short Codes: Shared among multiple businesses or organizations, offering a cost-effective solution.
- Random Short Codes: Randomly assigned short codes, often used for testing or temporary campaigns.
Key Players in the Short Code Ecosystem
- Carriers: Mobile network operators that deliver SMS messages to recipients.
- Short Code Providers: Companies that manage and lease short codes to businesses and individuals.
- Aggregators: Companies that facilitate the sending and receiving of SMS messages between businesses and carriers.
Benefits and Use Cases of SMS Short Codes
SMS short codes offer numerous benefits for businesses, including increased engagement, improved customer experience, enhanced marketing, and streamlined operations. By enabling two-way communication, short codes allow businesses to engage with customers and encourage feedback. They also provide a convenient and easy-to-use channel for customer support and queries, enabling targeted and personalized marketing campaigns that increase conversion rates and ROI. Additionally, short codes automate processes, such as appointment reminders and notifications, reducing manual workload.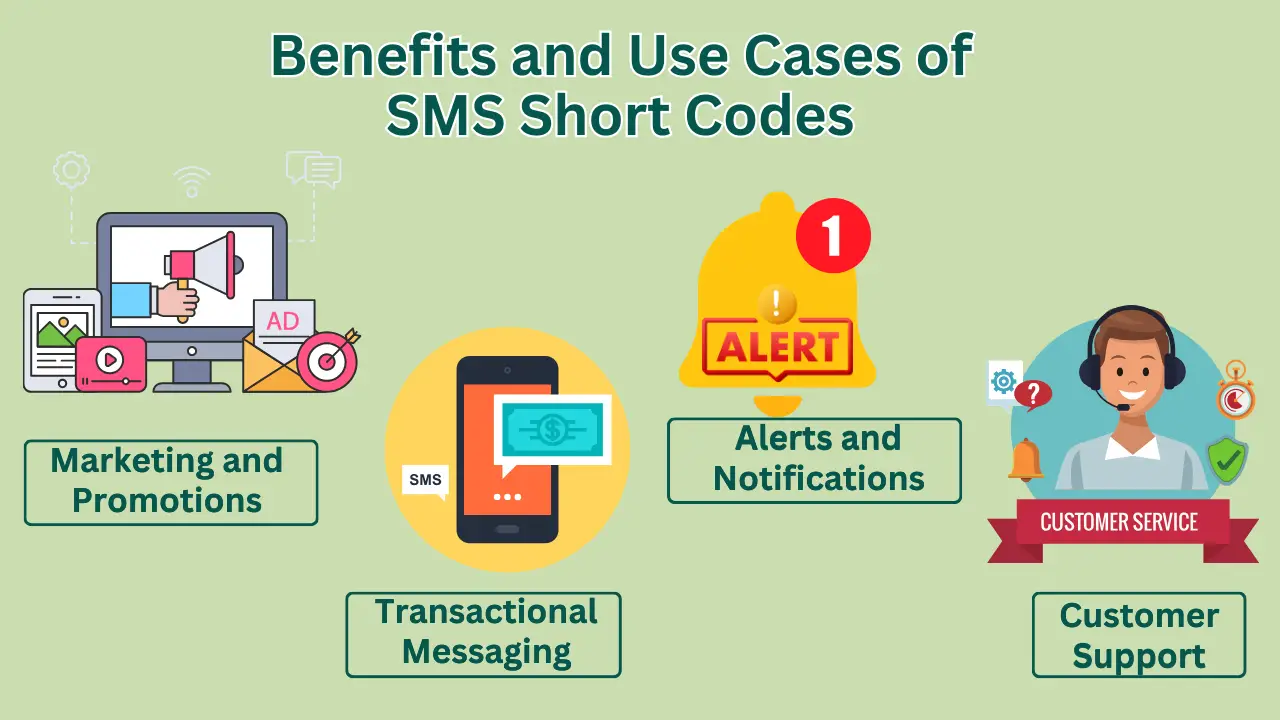
Use Cases for Businesses
Use Case | Description |
Marketing and Promotions | Run targeted campaigns, offer exclusive deals, and promote products/services |
Customer Support | Provide easy access to support, enable feedback, and resolve queries |
Alerts and Notifications | Send reminders, updates, and critical information to customers |
Transactional Messaging | Enable secure and convenient transactions, such as password resets and account updates |
Individual Benefits
SMS short codes also offer benefits for individuals, including convenience, privacy, and control. Short codes are easy to remember and use, making it simple to interact with businesses. They also enable communication without revealing personal phone numbers, and individuals can opt-in/out of communications, controlling the flow of information.
Use Case | Description |
Customer Support | Easily access support and resolve queries |
Exclusive Offers | Receive personalized promotions and deals |
Important Alerts | Receive critical information, such as |
Best Practices for Implementing SMS Short Codes
Implementing SMS short codes requires careful consideration to maximize their effectiveness. The first step is to choose the right short code, which involves deciding between dedicated and shared short codes, as well as random and vanity short codes. Dedicated short codes offer exclusive use and full control, while shared short codes are cost-effective but shared among multiple users. Vanity short codes, on the other hand, are customizable and memorable, making them a great option for businesses looking to establish a strong brand identity.
Step 1: Choose the Right Short Code
When selecting a short code, consider whether a dedicated or shared short code best suits your needs. Dedicated short codes offer exclusive use and full control, while shared short codes are cost-effective but shared among multiple users. Additionally, decide between random short codes, which are automatically assigned, and vanity short codes, which are customizable and memorable.
Step 2: Set Up and Configure Short Codes
To set up and configure short codes, ensure compatibility with carriers, aggregators, and messaging platforms. Configure keywords for specific actions, such as “STOP” for opt-out. Define message routing, processing, and response handling to ensure seamless communication.
Step 3: Follow Content and Messaging Best Practices
Keep messages clear, concise, and relevant to engage your audience. Ensure clear opt-in and opt-out processes to respect customer preferences. Adhere to CTIA and TCPA guidelines, as well as carrier-specific rules, to maintain compliance.
Step 4: Manage and Optimize Campaigns
Monitor performance, track KPIs, and analyze results to optimize campaigns. Conduct A/B testing to refine messages, keywords, and campaigns. Collect and incorporate customer feedback to improve campaigns and enhance customer satisfaction.
Step 5: Address Security and Compliance Considerations
Ensure secure storage and transmission of customer data to protect sensitive information. Adhere to carrier-specific guidelines and regulations, as well as CTIA and TCPA compliance, to avoid penalties and maintain trust.
SMS Short Code Regulations and Compliance
SMS short code regulations and compliance are critical considerations for businesses looking to leverage the power of short codes. The Cellular Telecommunications Industry Association (CTIA) and the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) provide guidelines and regulations for SMS marketing, including obtaining prior express written consent from customers before sending messages. 
CTIA Guidelines
- Program Principles: Adhere to CTIA’s guidelines for SMS marketing, including transparency, choice, and security.
- Messaging Principles: Follow CTIA’s guidelines for messaging, including clear and concise messages.
TCPA Regulations
- Prior Express Written Consent: Obtain explicit consent from customers before sending SMS messages.
- Opt-out Requirements: Provide clear opt-out instructions and honor requests.
Carrier-Specific Regulations
- AT&T: Adhere to AT&T’s guidelines for SMS marketing, including restrictions on promotional content.
- Verizon: Follow Verizon’s guidelines for SMS marketing, including requirements for opt-in and opt-out processes.
- T-Mobile: Comply with T-Mobile’s guidelines for SMS marketing, including restrictions on message frequency.
Best Practices for Compliance
- Keep Records: Maintain records of customer consent, opt-out requests, and message logs.
- Monitor Compliance: Regularly review and update compliance processes to ensure adherence to regulations.
- Train Staff: Educate staff on compliance requirements and best practices.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Fines and Penalties: Face fines and penalties for non-compliance with CTIA, TCPA, and carrier regulations.
- Reputation Damage: Risk damaging your reputation and losing customer trust.
- Program Suspension: Face suspension or termination of your SMS program.
Measuring the Success of SMS Short Code Campaigns
To measure the success of SMS short code campaigns, it’s essential to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics for success. KPIs include delivery rate, open rate, response rate, and conversion rate, which provide insights into the campaign’s reach, engagement, and effectiveness. Metrics for success, such as return on investment (ROI), cost per acquisition (CPA), and customer lifetime value (CLV), help evaluate the campaign’s financial performance and customer value.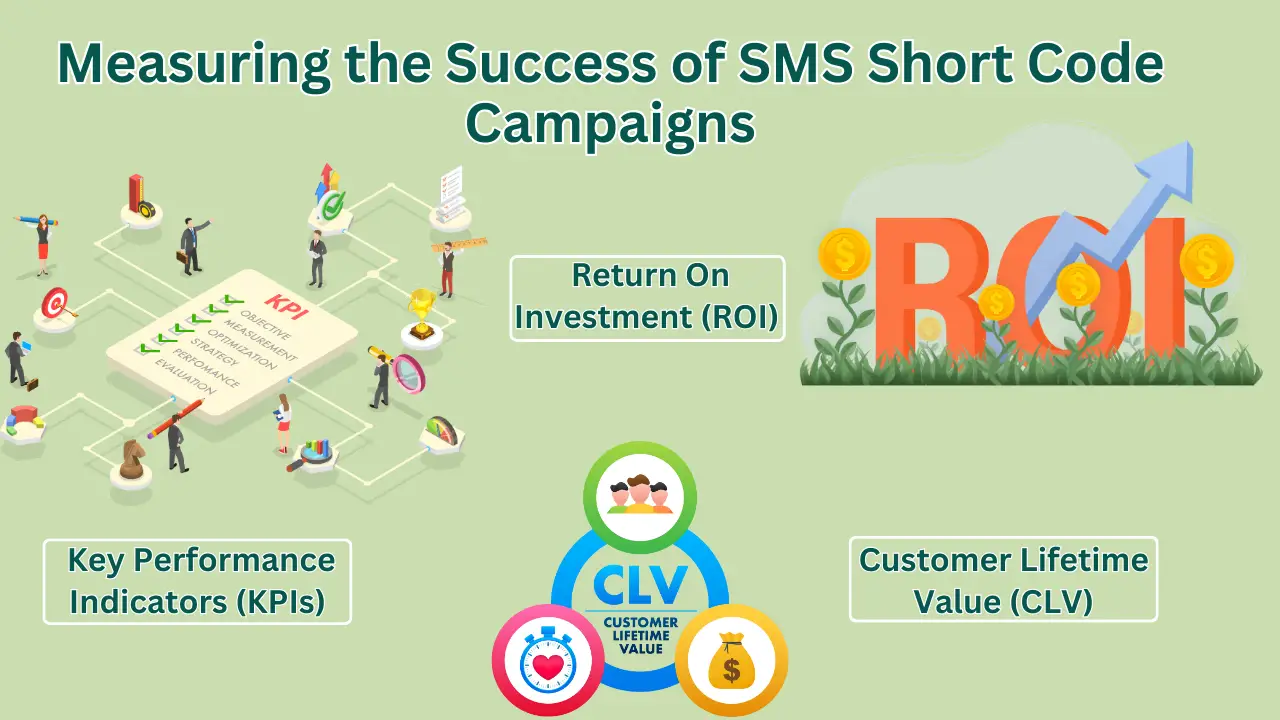
Tracking and Analysis Tools
To track and analyze SMS campaign performance, businesses can utilize various tools, including:
- Google Analytics: Track website traffic and conversions generated by SMS campaigns
- SMS Platform Analytics: Leverage built-in analytics tools provided by SMS platforms to track KPIs and metrics
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: Integrate SMS data with CRM software to track customer interactions and behavior
A/B Testing and Optimization
A/B testing and optimization are crucial to refining SMS campaign performance. Businesses can test different messages, keywords, and campaigns to optimize performance, as well as test different audience segments and send times to optimize targeting and engagement. By continually testing and optimizing, businesses can improve campaign results and achieve their marketing goals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with SMS Short Codes
When implementing SMS short codes, businesses must be aware of common technical, strategic, and compliance mistakes that can hinder campaign success. Technical mistakes include incorrect keyword configuration, insufficient message testing, and inadequate carrier coverage, which can lead to message routing issues, errors, and delivery problems. 
Technical Mistakes
When implementing SMS short codes, businesses must be aware of common technical mistakes that can hinder campaign success. Incorrect keyword configuration can lead to message routing issues, while insufficient message testing can result in errors and formatting problems. Additionally, inadequate carrier coverage can cause delivery issues, highlighting the importance of provisioning short codes with all major carriers.
Strategic Mistakes
Strategic mistakes can also undermine SMS campaign effectiveness. Poor opt-in and opt-out processes can lead to customer frustration, while inadequate message personalization can result in generic and irrelevant content. Over-messaging is another common mistake, causing customer fatigue and opt-outs. By avoiding these strategic mistakes, businesses can ensure their SMS campaigns resonate with customers and achieve desired outcomes.
Compliance Mistakes
Compliance mistakes can have serious consequences, including fines and penalties. Inadequate consent collection, non-compliance with CTIA and TCPA guidelines, and inadequate record keeping can all lead to compliance issues. By prioritizing compliance and maintaining accurate records, businesses can avoid these mistakes and ensure their SMS campaigns operate within regulatory boundaries.
Best Practices to Avoid Mistakes
To avoid mistakes and ensure SMS campaign success, businesses should regularly review and update their processes to stay current with industry changes and best practices. Conducting regular testing and quality assurance can also help identify and rectify errors, while monitoring customer feedback can provide valuable insights to improve campaigns and avoid mistakes. By following these best practices, businesses can maximize the effectiveness of their SMS short code campaigns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SMS short codes offer a powerful channel for businesses and individuals to connect with their audience. By understanding the benefits, use cases, and best practices outlined in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of SMS short codes and drive success in your marketing, customer support, and engagement efforts. Remember to stay compliant with industry regulations, avoid common mistakes, and continually monitor and optimize your campaigns to achieve maximum ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions
An SMS Short Code is a special 5-6 digit phone number used for sending and receiving SMS messages, ideal for marketing campaigns, customer support, and alerts.
SMS Short Codes offer convenience, speed, and reach, making them ideal for businesses to connect with customers, drive conversions, and boost brand loyalty.
Choose between dedicated, shared, random, or vanity short codes based on your business needs. Consider factors like exclusivity, cost, and brand identity.
Obtain prior express written consent from customers, provide clear opt-out instructions, and adhere to CTIA, TCPA, and carrier-specific guidelines to avoid fines and penalties.
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like delivery rate, open rate, response rate, and conversion rate, and use analytics tools like Google Analytics, SMS Platform Analytics, or CRM Software to evaluate campaign effectiveness.



